MetaAuthIAM secures systems with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and robust Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), enforcing tailored authorization policies for seamless, role-specific access to critical resources.
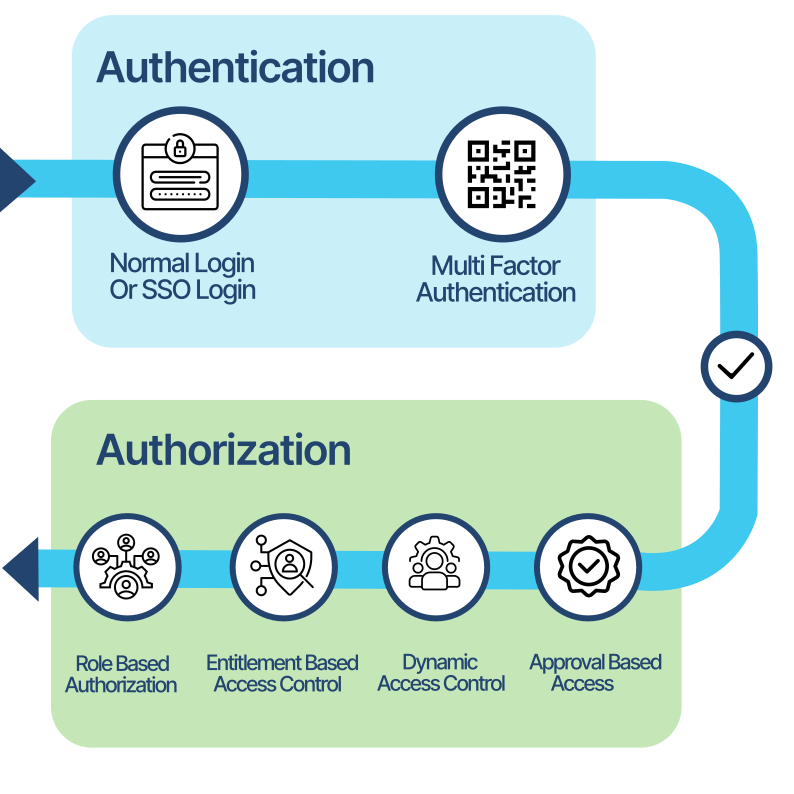
MetaAuthIAM enhances security through Multi-Factor Authentication MFA, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing critical systems
Through username and password user can do self login and access their account.
After basic authentication, MetaAuthIAM prompts the user to provide a second factor, such as an TOTP generated by an authenticator app or delivered OTP via email based on admin configuration.
Once both factors are verified, the user is granted access.
MetaAuthIAM supports Single Sign-On SSO, allowing users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications without needing to log in again for each one. This enhances user experience and reduces password fatigue while maintaining high security.
MetaAuthIAM supports OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect for integrating modern applications with SSO capabilities.

MFA and SSO reduce the risk of unauthorized access by strengthening identity verification.

SSO simplifies the login process for users, improving the user experience while maintaining security.
Supports a wide range of authentication mechanisms, making it adaptable to diverse organizational needs.
RBAC is a cornerstone of MetaAuthIAM's authorization model. Users are assigned specific roles that dictate their permissions across systems and applications. Each role encapsulates a set of entitlements, such as access to specific resources, applications, or services.
Administrators create roles based on organizational responsibilities (e.g., Admin, Manager, Employee).
Users are assigned roles based on their job function, department, or access needs.
When a user attempts to access a resource, MetaAuthIAM checks their assigned roles to determine if the action is allowed.
Entitlements define the specific actions or resources a user can access within an application. MetaAuthIAM allows administrators to assign fine-grained entitlements to users based on their roles or attributes. For example, an entitlement may grant a user the ability to access a particular module in an enterprise application, such as viewing reports or managing transactions.
Administrators define specific entitlements that correspond to actions within integrated applications (e.g., read, write, approve).
Entitlements are assigned to users based on roles, attributes, or through direct assignment.
When users request access to a resource, MetaAuthIAM verifies if they hold the necessary entitlements to perform the requested action.
MetaAuthIAM supports Dynamic Access Control, which adjusts permissions in real time based on changing conditions or user behavior. For example, access to certain sensitive resources can be restricted based on location, time of day, or abnormal activity, further enhancing security.
MetaAuthIAM provides workflow-driven, approval-based access control. For sensitive resources or high-privilege actions, the platform enforces approval workflows, requiring access requests to be reviewed and approved by designated approvers before access is granted.
By combining RBAC with entitlement-based access, MetaAuthIAM enables administrators to define highly specific permissions.
MetaAuthIAM's authorization framework scales to accommodate complex environments with numerous applications and user roles.
Dynamic access and approval workflows ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive resources, minimizing the risk of unauthorized actions.